A new Nature Reviews Drug Discovery article by Linda Zhang, Jiangbo Wei, Zhongyu Zou, and Chuan He highlights how chemical modifications on RNA molecules—long known to fine-tune gene expression—are rapidly emerging as promising therapeutic targets.
For decades, most drug discovery has focused on DNA and proteins. But growing evidence shows that RNA—the messenger molecule that translates genetic information into proteins—also carries chemical marks that finely control gene expression. More than 170 types of RNA modifications have been identified, and researchers are now uncovering how they shape cell fate, disease progression, and therapeutic response.
Targeting RNA modifications could revolutionize cancer treatment, immunotherapy, and regenerative medicine,” the authors note. “This is not just epigenetics—it’s the rise of epitranscriptomic therapeutics.
Zhang et al. (2025)
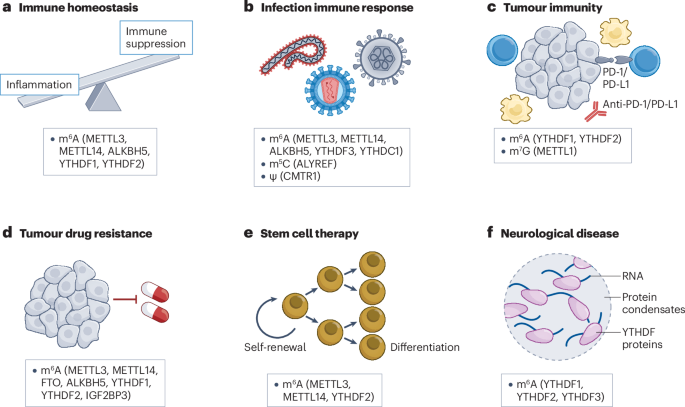
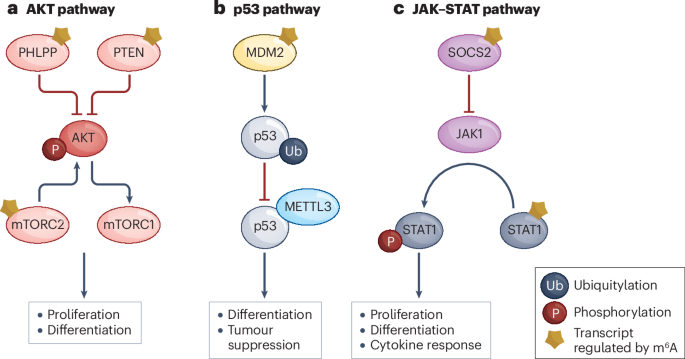
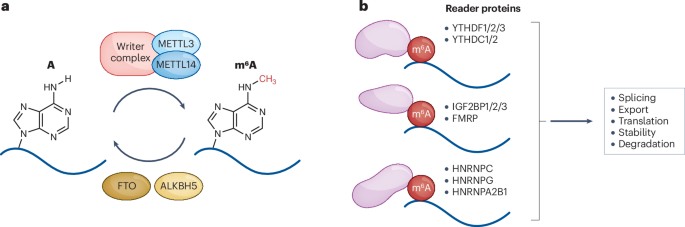
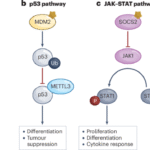
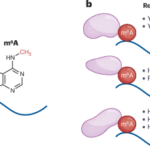
Among these, N⁶-methyladenosine (m⁶A) stands out as the most abundant and influential. Added by the enzyme complex METTL3–METTL14 (“writers”) and removed by FTO or ALKBH5 (“erasers”), m⁶A modifications act as dynamic regulators of mRNA translation, stability, and degradation. Specialized “reader” proteins—such as YTHDF1–3 and IGF2BP—interpret these chemical marks to determine whether a gene is turned on or off at the RNA level.
Dysregulated m⁶A pathways have now been linked to cancer, immune dysfunction, neurological disease, and viral infection. For example, overactive METTL3 or FTO enzymes can drive leukemia and glioblastoma by enhancing oncogene translation, while inhibiting them reverses tumor growth in animal models. These findings have spurred pharmaceutical companies to pursue RNA modification enzymes as novel therapeutic targets.
One such compound, STC-15, is the world’s first METTL3 inhibitor to reach clinical trials (NCT05584111), aimed at treating solid tumors. Preclinical data show it can suppress leukemia growth and boost anti-tumor immune responses without harming normal cells. Other inhibitors—such as FB23-2 (FTO inhibitor) and DC-Y13-27 (YTHDF2 inhibitor)—have demonstrated synergy with immunotherapies like anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 drugs, suggesting RNA modification targeting could enhance existing cancer treatments.
Beyond m⁶A, the review also discusses several other promising RNA marks:
- m⁷G (N7-methylguanosine), crucial for tRNA and mRNA stability, regulated by METTL1/WDR4.
- m⁵C (5-methylcytosine), written by NSUN and TRDMT1 enzymes, linked to cancer metabolism and DNA repair.
- m¹A (N1-methyladenosine) and pseudouridine (Ψ), which influence translation fidelity and stress responses.
- 2′-O-methylation (Nm), important for distinguishing self from viral RNA and preventing autoimmune activation.
The authors emphasize that while progress is exciting, developing selective, safe inhibitors remains challenging. Many enzymes share similar catalytic pockets, making off-target effects likely. They propose that allosteric inhibitors, RNA-targeted antisense oligonucleotides, and CRISPR-based RNA editors could allow for more precise manipulation of specific RNA sites.
The review concludes that understanding and modulating RNA modifications could reshape modern medicine — from cancer and infectious diseases to stem cell therapy and vaccine design. Indeed, the success of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, which used the modified base N¹-methylpseudouridine to improve stability and translation, is a testament to the clinical power of RNA chemistry.








this is an amazing IDEA
Nice article